In rare cases, the solstice may occur as early as December 20 or as late as December 23. According to timeanddate.com. To avoid confusion between different time zones, the official time of the solstice is based on Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), which is five hours ahead of Eastern Time. By that standard, the last time a December 23rd occurred a century ago — in 1903 — wouldn’t occur again until 2303. The solstice, which begins on December 20, will occur as early as 2080.
What does winter solstice mean?
The December solstice marks the beginning of astronomical winter in the Northern Hemisphere. During the solstice, the midday sun appears Done directly The Tropic of Capricorn is a line of latitude 23.5 degrees south of the Earth’s equator. It is the southern point where the sun is directly visible (90 degrees above the horizon).
In the Northern Hemisphere, we see the Sun taking it Low and short path Across the southern sky. A low sun angle means you’ll cast the longest afternoon shadow of the year on the winter solstice, assuming the sky is clear.
The word “moon” comes from the Latin word solstitium, meaning “standing sun”. At the December solstice, the sun’s daily southward movement across the sky appears to have paused, and the sun rises and sets at its southernmost points on the horizon. After the solstice, the position of sunrise and sunset moves northward again, and we slowly begin to gain daylight.
Why do we have a solstice?
The solstices and seasons occur because the Earth does not revolve completely around the Sun. Conversely, the Earth’s axis is tilted about 23.5 degrees from the vertical, causing each hemisphere to receive different amounts of sunlight throughout the year.
In December, the Northern Hemisphere tilts away from the Sun, bringing us less direct sunlight and cooler weather. Meanwhile, in the Southern Hemisphere, December 21 is the first day of astronomical summer and the longest day of the year. The equinoxes, between the winter and summer solstices, mean that the length of day and night are nearly equal everywhere on Earth.
Although the winter solstice is often referred to as the “first day of winter,” there are different ways to define the start and end date of the season. December 21 is the first day of astronomical winter in the Northern Hemisphere, which lasts until the vernal equinox in March. However, the weather winter corresponds to the three coldest months of the calendar year and lasts from December 1 to the end of February.
Solar winter, defined as the darkest three months of the year, begins in early November and lasts until early February. Many ancient cultures considered the winter solstice to be “Midwinter” because it occurs halfway through the dark calendar quarter of the year.
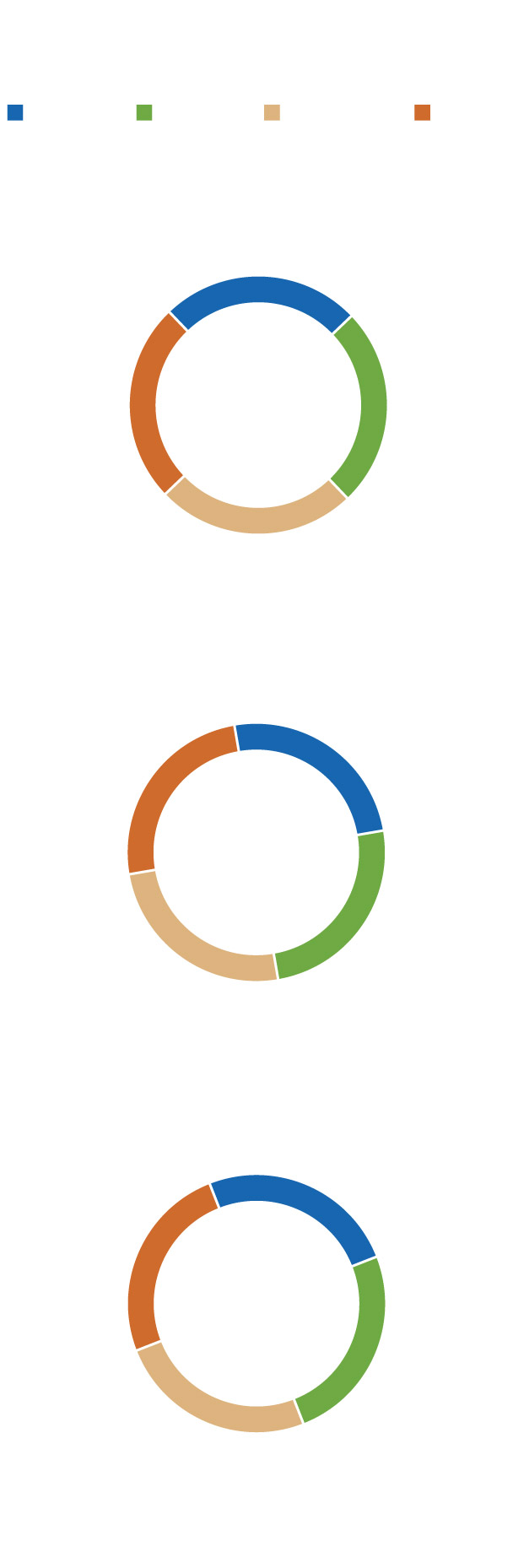
Three ways to define a season
In the Northern Hemisphere
Sun light
In terms of length
Day* per year
Astronomy
Based on the position of
Earth associated with Sun*
Meteorology
On calendar and average basis
Annual temperature
*Exact dates may vary slightly from year to year.
Nick Mourtoubalas/Washington Post
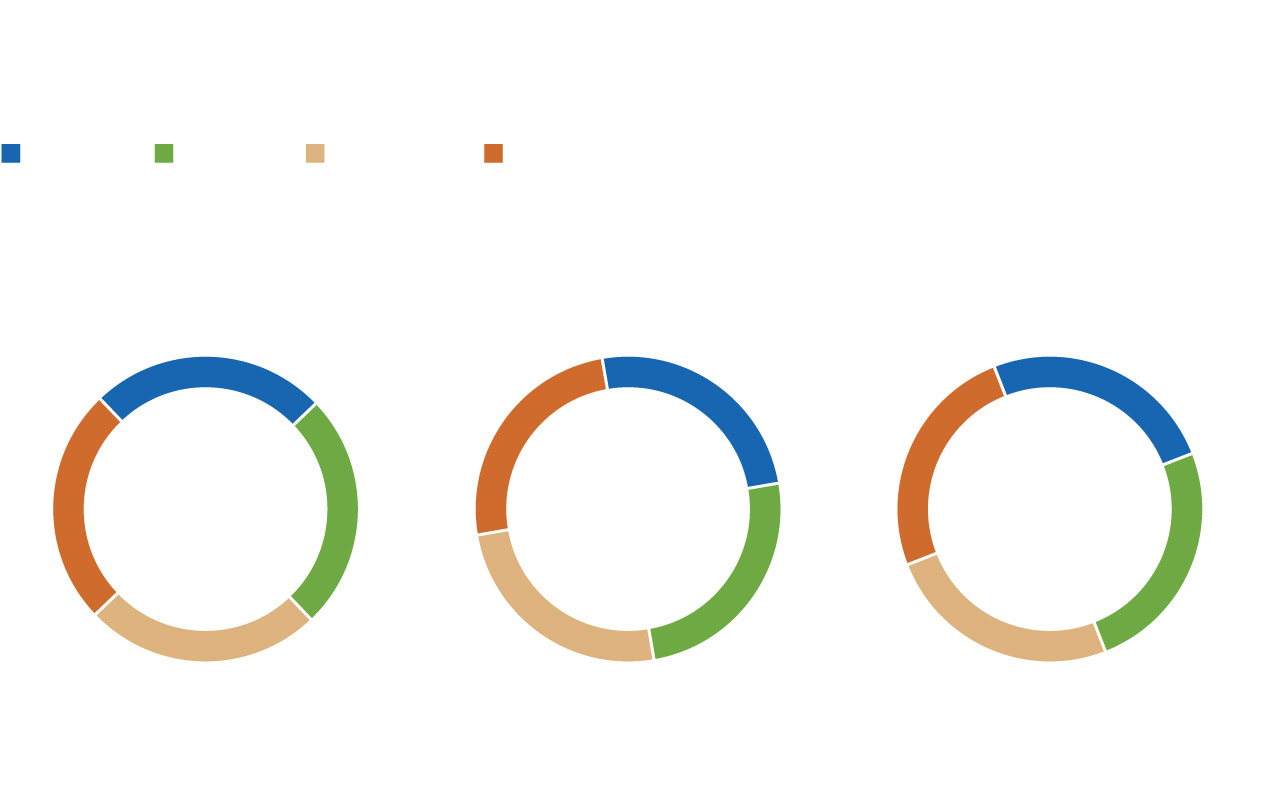
Three ways to define a season
In the Northern Hemisphere
Sun light
In terms of length
Day* per year
Astronomy
Based on the position of
Earth associated with Sun*
Meteorology
On calendar and average basis
Annual temperature
*Exact dates may vary slightly from year to year.
Nick Mourtoubalas/Washington Post
When is the shortest day of the year?
The Short day The time of year in the Northern Hemisphere is always at the winter solstice. However, the earlier sunset and the latest sunrise of the year do not occur on the same day. DC sees 9 hours and 26 minutes of daylight on December 21 (sunrise at 7:23 AM and sunset at 4:49 PM). However, the earliest sunset is at 4:45 PM on December 7 and the latest sunrise is at 7:27 AM on January 5.
Exact dates of earliest sunset and latest sunrise Depends on one’s latitude. In the lower 48, the latest sunset and latest sunrise occur two weeks before and after the solstice, respectively. Near the Arctic Circle, the earliest sunset and latest sunrise occur on or around December 21.
When will the days get longer?
Like a swinging pendulum, daylight begins to increase once we pass the solstice, although you may not notice it at first. DC loses less than one second of daylight on December 22, but gains four seconds of light on December 23. According to timeanddate.com. In early January, daylight increases by more than 30 seconds per day.
Cities at higher latitudes near the North Pole begin to receive sunlight more rapidly. In AnchorIn the first week of January daylight starts to increase to more than two minutes per day.
How is winter solstice celebrated?
Human beings Throughout history They celebrated the solstices with rituals such as bonfires and ceremonial dances to mark the passing of the seasons. The ancient Romans held a week-long pagan festival SaturnDedicated to the god of time and agriculture, it celebrates the return of the sun’s light on December 17.
The modern-day connection between Christmas and “Yule” comes from the vernacular word jal, A pre-Christian winter solstice festival held in Scandinavia. According to timeanddate.com, the custom of lighting the Yule log at Christmas is believed to have originated in the bonfires associated with the festival of Joule.
Many prehistoric monuments and landmarks around the world were built to represent the sun’s changing path in the sky. Built over 5,000 years ago in modern England, Stonehenge is perhaps the most famous of these prehistoric landmarks. Some historians say that there was once a large circle of free-standing stones Solar calendar Used to track seasons. Today, thousands gather at Stonehenge every year to celebrate the solstices, equinoxes and the changing of the seasons.
